thanksRaccoon stealer is an example of malware that specializes in stealing sensitive information from infected computers. Once installed, Raccoon can collect a wide range of data, including browser history, passwords, cookies, credit card information, and cryptocurrency wallet information. This information is then sent to a remote server controlled by the malware operators.
What is a Raccoon Stealer?
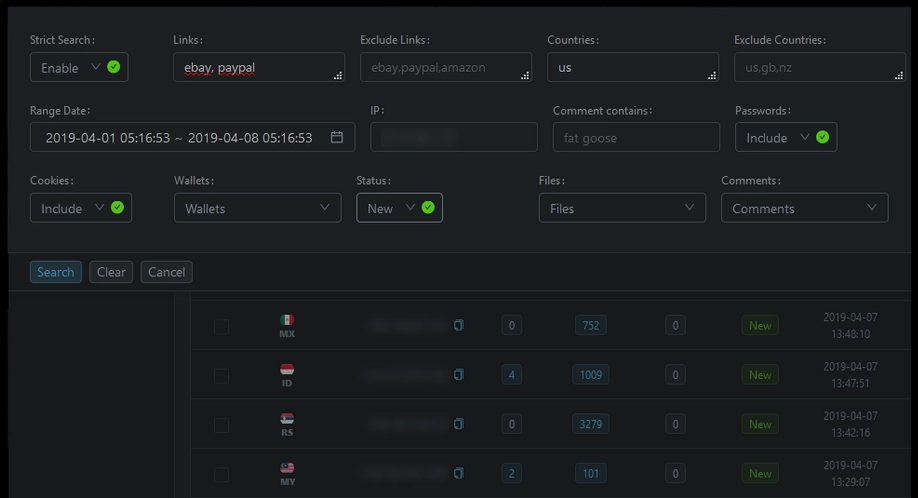 Raccoon has been involved in numerous high-profile attacks on organizations worldwide. Its success is partly due to its use of advanced anti-detection techniques, such as sandbox bypass and code obfuscation, making it difficult for security researchers to analyze and detect it. In addition, malware is constantly evolving. It can work as standalone or complementary malware, and developers of this malware publish extensive messages on relevant forums where they advertise their brainchild.
Raccoon has been involved in numerous high-profile attacks on organizations worldwide. Its success is partly due to its use of advanced anti-detection techniques, such as sandbox bypass and code obfuscation, making it difficult for security researchers to analyze and detect it. In addition, malware is constantly evolving. It can work as standalone or complementary malware, and developers of this malware publish extensive messages on relevant forums where they advertise their brainchild.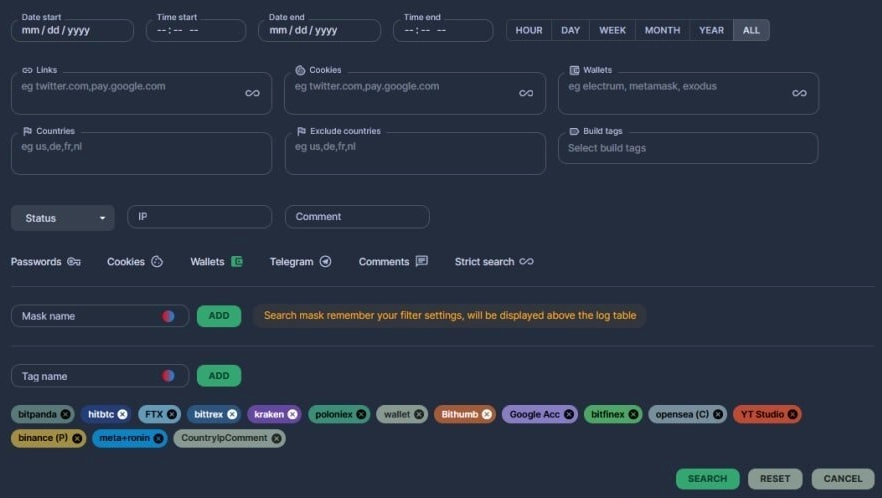
In addition to its primary purpose, Raccoon Stealer can act as a downloader, making it versatile for downloading specific files to a victim’s system and using a botnet of Raccoon-infected PCs. Furthermore, each malware sample is uniquely built, making it difficult for security tools to detect. Although both versions use base64 encoding, version 2 includes RC4 encryption with a hard-coded decryption key in the malware executable. The new version also inserts several unnecessary codes into the malware code, making reverse-engineering analysis difficult. In addition, the malware requires additional dynamic link libraries, which it receives from the command and control server during the initial data exchange to decrypt and save data.
How does it work?
The latest version of Raccoon Stealer has a packaging and encryption feature by default. In contrast, the previous version did not have these detection protections. In addition, the new version includes anti-VM and anti-sandboxing features. However, despite the implementation of these measures, there were cases where the latest version arrived on target systems in unpacked form, indicating that it is possible to disable these features when generating samples.
C2 communicationRaccoon Stealer uses a predefined list of IP addresses to connect to its command and control server. However, obtaining these IP addresses was different in the first version than in the second: the first version of Raccoon Stealer sent a request to the Telegram messenger and got a list of C2 addresses from there. The new version contains a list of hardcoded C2 addresses, which is added at the stage of malware generation. When Raccoon Stealer first contacts the command and control server, it receives DLLs and configuration files. The malware then resets the collected information and sends a POST request with the parameters bot_id and config_id. The libraries of the first version are slightly different from the second. *** Hidden text: cannot be quoted. ***
-
💌Important Message to All Fellas💌 💌Important Message to All Fellas 💌
⚠️Thank you for being with us over the past year.
To support our community, we're now offering an "Account Upgrade" for purchase.
VIP and Legendary members get special direct downloads without needing to like or reply to threads. Upgrade now to enjoy these benefits!
HERE Our Official Telegram⛔ Spam: If someone try SCAM you or SPAM Message to you let me know we will ban them
🏆 Download Error or Missing Link: Click on threads and report them to Our admin will re-upload for you.
☣️ Infected or Backdoor/RAT: If you find a virus, please report it to us via Telegram or click report in the threads, and we will completely ban them in 100%
🎯 Our Plan : Make resource downloads on a private host without using another free upload because easy gone
❤️ We try our best to make everyone's shared tools clean and fresh in here, so enjoy with our fellas. ❤️
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
- Status
- Not open for further replies.
thanksRaccoon stealer is an example of malware that specializes in stealing sensitive information from infected computers. Once installed, Raccoon can collect a wide range of data, including browser history, passwords, cookies, credit card information, and cryptocurrency wallet information. This information is then sent to a remote server controlled by the malware operators.
What is a Raccoon Stealer?
 Raccoon has been involved in numerous high-profile attacks on organizations worldwide. Its success is partly due to its use of advanced anti-detection techniques, such as sandbox bypass and code obfuscation, making it difficult for security researchers to analyze and detect it. In addition, malware is constantly evolving. It can work as standalone or complementary malware, and developers of this malware publish extensive messages on relevant forums where they advertise their brainchild.
Raccoon has been involved in numerous high-profile attacks on organizations worldwide. Its success is partly due to its use of advanced anti-detection techniques, such as sandbox bypass and code obfuscation, making it difficult for security researchers to analyze and detect it. In addition, malware is constantly evolving. It can work as standalone or complementary malware, and developers of this malware publish extensive messages on relevant forums where they advertise their brainchild.
In addition to its primary purpose, Raccoon Stealer can act as a downloader, making it versatile for downloading specific files to a victim’s system and using a botnet of Raccoon-infected PCs. Furthermore, each malware sample is uniquely built, making it difficult for security tools to detect. Although both versions use base64 encoding, version 2 includes RC4 encryption with a hard-coded decryption key in the malware executable. The new version also inserts several unnecessary codes into the malware code, making reverse-engineering analysis difficult. In addition, the malware requires additional dynamic link libraries, which it receives from the command and control server during the initial data exchange to decrypt and save data.
How does it work?
The latest version of Raccoon Stealer has a packaging and encryption feature by default. In contrast, the previous version did not have these detection protections. In addition, the new version includes anti-VM and anti-sandboxing features. However, despite the implementation of these measures, there were cases where the latest version arrived on target systems in unpacked form, indicating that it is possible to disable these features when generating samples.
C2 communicationRaccoon Stealer uses a predefined list of IP addresses to connect to its command and control server. However, obtaining these IP addresses was different in the first version than in the second: the first version of Raccoon Stealer sent a request to the Telegram messenger and got a list of C2 addresses from there. The new version contains a list of hardcoded C2 addresses, which is added at the stage of malware generation. When Raccoon Stealer first contacts the command and control server, it receives DLLs and configuration files. The malware then resets the collected information and sends a POST request with the parameters bot_id and config_id. The libraries of the first version are slightly different from the second. *** Hidden text: cannot be quoted. ***
G
Great, ty Sharing is CaringRaccoon stealer is an example of malware that specializes in stealing sensitive information from infected computers. Once installed, Raccoon can collect a wide range of data, including browser history, passwords, cookies, credit card information, and cryptocurrency wallet information. This information is then sent to a remote server controlled by the malware operators.
What is a Raccoon Stealer?
 Raccoon has been involved in numerous high-profile attacks on organizations worldwide. Its success is partly due to its use of advanced anti-detection techniques, such as sandbox bypass and code obfuscation, making it difficult for security researchers to analyze and detect it. In addition, malware is constantly evolving. It can work as standalone or complementary malware, and developers of this malware publish extensive messages on relevant forums where they advertise their brainchild.
Raccoon has been involved in numerous high-profile attacks on organizations worldwide. Its success is partly due to its use of advanced anti-detection techniques, such as sandbox bypass and code obfuscation, making it difficult for security researchers to analyze and detect it. In addition, malware is constantly evolving. It can work as standalone or complementary malware, and developers of this malware publish extensive messages on relevant forums where they advertise their brainchild.
In addition to its primary purpose, Raccoon Stealer can act as a downloader, making it versatile for downloading specific files to a victim’s system and using a botnet of Raccoon-infected PCs. Furthermore, each malware sample is uniquely built, making it difficult for security tools to detect. Although both versions use base64 encoding, version 2 includes RC4 encryption with a hard-coded decryption key in the malware executable. The new version also inserts several unnecessary codes into the malware code, making reverse-engineering analysis difficult. In addition, the malware requires additional dynamic link libraries, which it receives from the command and control server during the initial data exchange to decrypt and save data.
How does it work?
The latest version of Raccoon Stealer has a packaging and encryption feature by default. In contrast, the previous version did not have these detection protections. In addition, the new version includes anti-VM and anti-sandboxing features. However, despite the implementation of these measures, there were cases where the latest version arrived on target systems in unpacked form, indicating that it is possible to disable these features when generating samples.
C2 communicationRaccoon Stealer uses a predefined list of IP addresses to connect to its command and control server. However, obtaining these IP addresses was different in the first version than in the second: the first version of Raccoon Stealer sent a request to the Telegram messenger and got a list of C2 addresses from there. The new version contains a list of hardcoded C2 addresses, which is added at the stage of malware generation. When Raccoon Stealer first contacts the command and control server, it receives DLLs and configuration files. The malware then resets the collected information and sends a POST request with the parameters bot_id and config_id. The libraries of the first version are slightly different from the second. *** Hidden text: cannot be quoted. ***
tRaccoon stealer is an example of malware that specializes in stealing sensitive information from infected computers. Once installed, Raccoon can collect a wide range of data, including browser history, passwords, cookies, credit card information, and cryptocurrency wallet information. This information is then sent to a remote server controlled by the malware operators.
What is a Raccoon Stealer?
 Raccoon has been involved in numerous high-profile attacks on organizations worldwide. Its success is partly due to its use of advanced anti-detection techniques, such as sandbox bypass and code obfuscation, making it difficult for security researchers to analyze and detect it. In addition, malware is constantly evolving. It can work as standalone or complementary malware, and developers of this malware publish extensive messages on relevant forums where they advertise their brainchild.
Raccoon has been involved in numerous high-profile attacks on organizations worldwide. Its success is partly due to its use of advanced anti-detection techniques, such as sandbox bypass and code obfuscation, making it difficult for security researchers to analyze and detect it. In addition, malware is constantly evolving. It can work as standalone or complementary malware, and developers of this malware publish extensive messages on relevant forums where they advertise their brainchild.
In addition to its primary purpose, Raccoon Stealer can act as a downloader, making it versatile for downloading specific files to a victim’s system and using a botnet of Raccoon-infected PCs. Furthermore, each malware sample is uniquely built, making it difficult for security tools to detect. Although both versions use base64 encoding, version 2 includes RC4 encryption with a hard-coded decryption key in the malware executable. The new version also inserts several unnecessary codes into the malware code, making reverse-engineering analysis difficult. In addition, the malware requires additional dynamic link libraries, which it receives from the command and control server during the initial data exchange to decrypt and save data.
How does it work?
The latest version of Raccoon Stealer has a packaging and encryption feature by default. In contrast, the previous version did not have these detection protections. In addition, the new version includes anti-VM and anti-sandboxing features. However, despite the implementation of these measures, there were cases where the latest version arrived on target systems in unpacked form, indicating that it is possible to disable these features when generating samples.
C2 communicationRaccoon Stealer uses a predefined list of IP addresses to connect to its command and control server. However, obtaining these IP addresses was different in the first version than in the second: the first version of Raccoon Stealer sent a request to the Telegram messenger and got a list of C2 addresses from there. The new version contains a list of hardcoded C2 addresses, which is added at the stage of malware generation. When Raccoon Stealer first contacts the command and control server, it receives DLLs and configuration files. The malware then resets the collected information and sends a POST request with the parameters bot_id and config_id. The libraries of the first version are slightly different from the second. *** Hidden text: cannot be quoted. ***
Raccoon stealer is an example of malware that specializes in stealing sensitive information from infected computers. Once installed, Raccoon can collect a wide range of data, including browser history, passwords, cookies, credit card information, and cryptocurrency wallet information. This information is then sent to a remote server controlled by the malware operators.
What is a Raccoon Stealer?
 Raccoon has been involved in numerous high-profile attacks on organizations worldwide. Its success is partly due to its use of advanced anti-detection techniques, such as sandbox bypass and code obfuscation, making it difficult for security researchers to analyze and detect it. In addition, malware is constantly evolving. It can work as standalone or complementary malware, and developers of this malware publish extensive messages on relevant forums where they advertise their brainchild.
Raccoon has been involved in numerous high-profile attacks on organizations worldwide. Its success is partly due to its use of advanced anti-detection techniques, such as sandbox bypass and code obfuscation, making it difficult for security researchers to analyze and detect it. In addition, malware is constantly evolving. It can work as standalone or complementary malware, and developers of this malware publish extensive messages on relevant forums where they advertise their brainchild.
In addition to its primary purpose, Raccoon Stealer can act as a downloader, making it versatile for downloading specific files to a victim’s system and using a botnet of Raccoon-infected PCs. Furthermore, each malware sample is uniquely built, making it difficult for security tools to detect. Although both versions use base64 encoding, version 2 includes RC4 encryption with a hard-coded decryption key in the malware executable. The new version also inserts several unnecessary codes into the malware code, making reverse-engineering analysis difficult. In addition, the malware requires additional dynamic link libraries, which it receives from the command and control server during the initial data exchange to decrypt and save data.
How does it work?
The latest version of Raccoon Stealer has a packaging and encryption feature by default. In contrast, the previous version did not have these detection protections. In addition, the new version includes anti-VM and anti-sandboxing features. However, despite the implementation of these measures, there were cases where the latest version arrived on target systems in unpacked form, indicating that it is possible to disable these features when generating samples.
C2 communicationRaccoon Stealer uses a predefined list of IP addresses to connect to its command and control server. However, obtaining these IP addresses was different in the first version than in the second: the first version of Raccoon Stealer sent a request to the Telegram messenger and got a list of C2 addresses from there. The new version contains a list of hardcoded C2 addresses, which is added at the stage of malware generation. When Raccoon Stealer first contacts the command and control server, it receives DLLs and configuration files. The malware then resets the collected information and sends a POST request with the parameters bot_id and config_id. The libraries of the first version are slightly different from the second. *** Hidden text: cannot be quoted. ***
Raccoon stealer is an example of malware that specializes in stealing sensitive information from infected computers. Once installed, Raccoon can collect a wide range of data, including browser history, passwords, cookies, credit card information, and cryptocurrency wallet information. This information is then sent to a remote server controlled by the malware operators.
What is a Raccoon Stealer?
 Raccoon has been involved in numerous high-profile attacks on organizations worldwide. Its success is partly due to its use of advanced anti-detection techniques, such as sandbox bypass and code obfuscation, making it difficult for security researchers to analyze and detect it. In addition, malware is constantly evolving. It can work as standalone or complementary malware, and developers of this malware publish extensive messages on relevant forums where they advertise their brainchild.
Raccoon has been involved in numerous high-profile attacks on organizations worldwide. Its success is partly due to its use of advanced anti-detection techniques, such as sandbox bypass and code obfuscation, making it difficult for security researchers to analyze and detect it. In addition, malware is constantly evolving. It can work as standalone or complementary malware, and developers of this malware publish extensive messages on relevant forums where they advertise their brainchild.
In addition to its primary purpose, Raccoon Stealer can act as a downloader, making it versatile for downloading specific files to a victim’s system and using a botnet of Raccoon-infected PCs. Furthermore, each malware sample is uniquely built, making it difficult for security tools to detect. Although both versions use base64 encoding, version 2 includes RC4 encryption with a hard-coded decryption key in the malware executable. The new version also inserts several unnecessary codes into the malware code, making reverse-engineering analysis difficult. In addition, the malware requires additional dynamic link libraries, which it receives from the command and control server during the initial data exchange to decrypt and save data.
How does it work?
The latest version of Raccoon Stealer has a packaging and encryption feature by default. In contrast, the previous version did not have these detection protections. In addition, the new version includes anti-VM and anti-sandboxing features. However, despite the implementation of these measures, there were cases where the latest version arrived on target systems in unpacked form, indicating that it is possible to disable these features when generating samples.
C2 communicationRaccoon Stealer uses a predefined list of IP addresses to connect to its command and control server. However, obtaining these IP addresses was different in the first version than in the second: the first version of Raccoon Stealer sent a request to the Telegram messenger and got a list of C2 addresses from there. The new version contains a list of hardcoded C2 addresses, which is added at the stage of malware generation. When Raccoon Stealer first contacts the command and control server, it receives DLLs and configuration files. The malware then resets the collected information and sends a POST request with the parameters bot_id and config_id. The libraries of the first version are slightly different from the second. *** Hidden text: cannot be quoted. ***
thank you so muchRaccoon stealer is an example of malware that specializes in stealing sensitive information from infected computers. Once installed, Raccoon can collect a wide range of data, including browser history, passwords, cookies, credit card information, and cryptocurrency wallet information. This information is then sent to a remote server controlled by the malware operators.
What is a Raccoon Stealer?
 Raccoon has been involved in numerous high-profile attacks on organizations worldwide. Its success is partly due to its use of advanced anti-detection techniques, such as sandbox bypass and code obfuscation, making it difficult for security researchers to analyze and detect it. In addition, malware is constantly evolving. It can work as standalone or complementary malware, and developers of this malware publish extensive messages on relevant forums where they advertise their brainchild.
Raccoon has been involved in numerous high-profile attacks on organizations worldwide. Its success is partly due to its use of advanced anti-detection techniques, such as sandbox bypass and code obfuscation, making it difficult for security researchers to analyze and detect it. In addition, malware is constantly evolving. It can work as standalone or complementary malware, and developers of this malware publish extensive messages on relevant forums where they advertise their brainchild.
In addition to its primary purpose, Raccoon Stealer can act as a downloader, making it versatile for downloading specific files to a victim’s system and using a botnet of Raccoon-infected PCs. Furthermore, each malware sample is uniquely built, making it difficult for security tools to detect. Although both versions use base64 encoding, version 2 includes RC4 encryption with a hard-coded decryption key in the malware executable. The new version also inserts several unnecessary codes into the malware code, making reverse-engineering analysis difficult. In addition, the malware requires additional dynamic link libraries, which it receives from the command and control server during the initial data exchange to decrypt and save data.
How does it work?
The latest version of Raccoon Stealer has a packaging and encryption feature by default. In contrast, the previous version did not have these detection protections. In addition, the new version includes anti-VM and anti-sandboxing features. However, despite the implementation of these measures, there were cases where the latest version arrived on target systems in unpacked form, indicating that it is possible to disable these features when generating samples.
C2 communicationRaccoon Stealer uses a predefined list of IP addresses to connect to its command and control server. However, obtaining these IP addresses was different in the first version than in the second: the first version of Raccoon Stealer sent a request to the Telegram messenger and got a list of C2 addresses from there. The new version contains a list of hardcoded C2 addresses, which is added at the stage of malware generation. When Raccoon Stealer first contacts the command and control server, it receives DLLs and configuration files. The malware then resets the collected information and sends a POST request with the parameters bot_id and config_id. The libraries of the first version are slightly different from the second. *** Hidden text: cannot be quoted. ***
thank youRaccoon stealer is an example of malware that specializes in stealing sensitive information from infected computers. Once installed, Raccoon can collect a wide range of data, including browser history, passwords, cookies, credit card information, and cryptocurrency wallet information. This information is then sent to a remote server controlled by the malware operators.
What is a Raccoon Stealer?
 Raccoon has been involved in numerous high-profile attacks on organizations worldwide. Its success is partly due to its use of advanced anti-detection techniques, such as sandbox bypass and code obfuscation, making it difficult for security researchers to analyze and detect it. In addition, malware is constantly evolving. It can work as standalone or complementary malware, and developers of this malware publish extensive messages on relevant forums where they advertise their brainchild.
Raccoon has been involved in numerous high-profile attacks on organizations worldwide. Its success is partly due to its use of advanced anti-detection techniques, such as sandbox bypass and code obfuscation, making it difficult for security researchers to analyze and detect it. In addition, malware is constantly evolving. It can work as standalone or complementary malware, and developers of this malware publish extensive messages on relevant forums where they advertise their brainchild.
In addition to its primary purpose, Raccoon Stealer can act as a downloader, making it versatile for downloading specific files to a victim’s system and using a botnet of Raccoon-infected PCs. Furthermore, each malware sample is uniquely built, making it difficult for security tools to detect. Although both versions use base64 encoding, version 2 includes RC4 encryption with a hard-coded decryption key in the malware executable. The new version also inserts several unnecessary codes into the malware code, making reverse-engineering analysis difficult. In addition, the malware requires additional dynamic link libraries, which it receives from the command and control server during the initial data exchange to decrypt and save data.
How does it work?
The latest version of Raccoon Stealer has a packaging and encryption feature by default. In contrast, the previous version did not have these detection protections. In addition, the new version includes anti-VM and anti-sandboxing features. However, despite the implementation of these measures, there were cases where the latest version arrived on target systems in unpacked form, indicating that it is possible to disable these features when generating samples.
C2 communicationRaccoon Stealer uses a predefined list of IP addresses to connect to its command and control server. However, obtaining these IP addresses was different in the first version than in the second: the first version of Raccoon Stealer sent a request to the Telegram messenger and got a list of C2 addresses from there. The new version contains a list of hardcoded C2 addresses, which is added at the stage of malware generation. When Raccoon Stealer first contacts the command and control server, it receives DLLs and configuration files. The malware then resets the collected information and sends a POST request with the parameters bot_id and config_id. The libraries of the first version are slightly different from the second. *** Hidden text: cannot be quoted. ***
- Status
- Not open for further replies.